You just received an email, you open it and it turns out to be a message that says the following: “Your order is on its way, but there has been a problem and some personal information needs to be completed.” So far it may look completely normal, if it weren't for the fact that you are actually not expecting any packages. Does this situation sing a bell? We are undoubtedly facing a common case of phishing. It is a classic in the cyber world. And although it has been around on the network for many years, nowadays a multitude of attacks of this type are still being launched.
Scammers are the first to innovate in their tactics and every day we are faced with more real-looking attacks
But first and foremost, let's start at the very beginning, what is a phishing attack? It is a form of cybercrime that consists of sending emails that appear to be from a trustworthy provider but whose purpose is to manipulate and defraud the recipient and thus obtain confidential information.
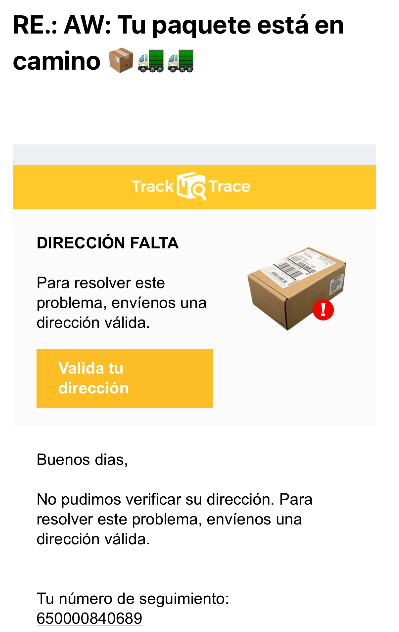
You may usually find messages alerting that there has been an error for example in the electricity bill and it is necessary to correct some data, or for example messages where the receiver has supposedly been awarded in a raffle of a well-known brand.
Although its most common means today is email, this type of attack is also carried out through WhatsApp or even SMS.
How to recognize that we are facing a phishing attack?
Scammers are the first to innovate in their tactics and every day we are faced with more real-looking attacks. However, we can always find clues that will help us recognize whether the message comes from a dangerous source.
The formula that phishing messages follow in most cases is the same, a story where they try to deceive the customer in order to make him click or open an attachment, thus activating the virus.
We talk about messages with content such as the following:
- Request to fill in some personal data.
- Including an invoice that turns out to be false.
- Offering a gift.
- Claiming that there is a problem with your account.
- Inform that you need to sign up through a link to receive a refund.
- Report suspicious activity detected or login that turns out to be fake.
Types of Phishing
- Deceptive Phishing: The most frequent one. Through this method, cybercriminals impersonate the identity of the victim (company or individual), it is usually not very personal and spreads out without a specific objective.
- Spear-phishing: They are defined by being highly personalized. While the goal is still to mislead the recipient, the message is more elaborate, detailing names and personal details that make it more difficult to detect.
- Whale-phishing: It is aimed primarily at CEOs or company emails, with the intention of obtaining access credentials. Once these data have been obtained, the criminal can impersonate the victim and authorize bank transfers or other high impact actions.
How can I protect myself against this type of attack?
- Protect your computer or mobile phone with a good security program.
- Do not provide financial or personal information by email. The companies that need them will not use this system to request them.
- Check the veracity of the web page from which you received the suspicious email.
- If you suspect that you may have been the victim of a phishing attack, immediately change all your passwords and contact the company or financial institution to inform them.
- Before clicking on suspicious links, manually type the address on your computer.
- When in doubt, do not risk it, the best advice against phishing is always to promote being cautious among all the people who are part of the organization. Ensuring the authenticity of content at the slightest suspicion is the best policy.
What are the most affected sectors?
According to a recent study by Panda Security, with the increase in teleworking and its consequent use of applications and office suites, it has been a major focus of phishing attempts, but there is more.
Transport and delivery companies are a sector that is seeing messages being popularized impersonating their name to make customers believe that they are receiving a package.
In addition, we can find this type of attack in internet payment services, streaming services, social networks and in different departments of the public administration, such as an error notice in the income tax return.




